英语时态基础入门知识(英语时态的详细知识急!!!!!!!!!)
1.英语时态的详细知识 急!!!!!!!!!
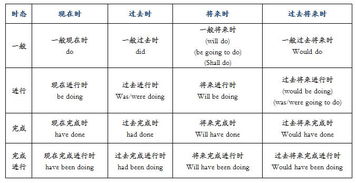
英语时态表一、概况一般时进行时完成时完成进行时一般现在时 现在进行时 现在完成时 现在完成进行时 一般过去时 过去进行时 过去完成时 过去完成进行时 一般将来时 将来进行时 将来完成时 将来完成进行时 一般过去将来时 过去将来进行时 过去将来完成时 过去将来完成进行时 二、十六种时态的谓语形势一般时态 进行时态 完成时态 完成进行时态 现在 do/does am/is/are doing have/has done have/has been doing 过去 did was/were doing had done had been doing 将来 shall/will do shall/will be doing shall/will have done shall/will have been doing 过去将来 should/would do should/would be doing should/would have done should/would have been doing 八种时态介绍:一 一般现在时态:表示现在经常发生或习惯性的动作。
时间状语: every …, sometimes, always, never, often, usually等。1 由be的is am are表示,之后接名词,形容词或介词。
陈述句:I am an office worker. He is so lazy. They are at home now.否定句: I am not Tim. She is not very beauiful. They are not in the office.一般疑问句:Are you an office assistant? Is she beautiful?特殊疑问句:What is your job? What colour is your bag?Where are you now?2 由实意动词V构成,引导疑问句和否定句,用do或don't。第三人称时用does或doesn't,有does出现动词用原形;第三人称陈述句V后加s或es.陈述句:I work in Shanghai. He works at home.Davy never watches TV at home.否定句: I don't like the food in KFC. Davy doesn't like the food in KFC either.一般疑问句: Do you want a cup of coffee? Does she live near the subway station?特殊疑问句:What do you want? Where does she live? How do they go to work?3 由情态动词can, must, may构成。
may没有否定形式。陈述句: I can drive a car. He must tell the truth. We may get there on foot.否定句:I can't swim at all. You mustn't(表示禁止) smoke in the office.一般疑问句: Can you wait a minute? Must I stay at home? May I use your phone?特殊疑问句: How can I get there? What must I do now?二 一般过去时态。
在过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。 时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hour ago,the day before yesterday,in 1997。
1由 be的过去式是 was或 were表示。Is\ am---was;are---were.陈述句:I was a big boss.He was beautiful. We were in Beijing last year.否定句: I was not at home at that moment. We were not at work yesterday.一般疑问句: Were you a teacher? Was she in the office last week?特殊疑问句:Where were you last night? When were you in that company?2 由V的过去式构成陈述句,疑问句和否定句用借助于did,有did出现动词用原形。
陈述句:I worked in Sunmoon.We studied English there. He lived in HongKong.否定句: I didn't work here. They didn't see me. She liked English a lot.一般疑问句: Did you go to America? Did he work in Sunmoon?特殊疑问句:Where did you work? What did he say to you? How did you know my name?3 由情态动词的过去式构成,can—could.She could walk when she was one year old. I could not speak English one year ago.三 一般将来时态:即将发生动作或状态。时间状语有:tomorrow,next year,the month after next,in two hours.1 任何人称+will+动词原形.I will fly to KongKong tomorrow. He will go with us. We will arrive in Shanghai next week.I will never believe you again. He will not come tonight. We will not buy a car next year.Will you go there by train? Will he come tomorrow? Will they live a five-star hotel?What will you do after class? Where will he live? How will they come here?2 is/am/are+going to+V原形,表示计划打算做什么事情。
I'm going to go to Kongkong by air. We are not going to buy a house here.Are they going to change their jobs? How are you going to tell him?四 过去将来时态;在过去将会发生的动作。构成:任何人称+would +V原形was/were going to +V原形He said he would come in in Shanghai. I sai I would buy you a car one day.They told me that they were not going to go abroad.五 现在进行时态:表示现在( 指说话人说话时) 正在发生的事情。
常用的时间的动作:now, at the(this)moment构成:is/am/are+Ving I'm waiting for my boy friend. He is doing the housework at home now.He is not playing toys. We are enjoying ourselves.Are you having dinner at home? Is Tim cooking in the kitchen?What are you doing now? Where are they having a meal?六 过去进行时态:过去一段时间正在发生的动作。构成:was/were+Ving I was doing my homework at that time. He was not sleeping at 11 o'clock last night.What were you doing at that moment?We were having a party while my neighbour is sleeping.七 现 在完成时态:用来表示之前已发生或完成的动作或状态,其结果的确和现在有联系。
动作或状态发生在过去但它的影响。
2.求英语八种基本时态的知识点及基础练习和强化练习(附答案)
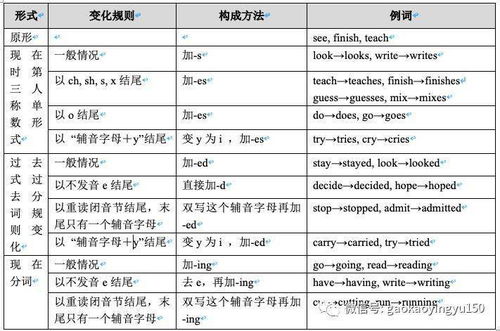
一般现在时表示习惯性、个人能力、普遍真理;表示“已经列入日程表”时常用一般现在时表示将来;2.表示说话人始料的事,常用一般过去时;3.进行时与某些频度副词连用时,常带有赞赏、厌烦等感情色彩;4.时间状语从句或条件状语从句中常用一般时表将来;5.will/be going to do/be about to do的用法区别;6.固定句式中的时态搭配;7.用主动形式表示被动意义常见的几种情况;8.was/were going to do以及had intended/hoped/expected/thought等可表示本打算干某事,实际上未干成;9.固定句式中的时态:1)It/This is/was+the+序数词+time+that-----; It/This is/was+the+形容词最高级+名词+ -----2)hardly/scarcely----when,no sooner---than结构中when,than前的主句必须用过去完成时时than,when所在的从句用一般过去时;3)It is(high)time that-----(早)该----结构中,从句谓语动词必须用过去时,是虚拟语气的一种;4)It will be+一段时间+before+从句(从句谓语动词一般用现在时) It was+一段时间+before+从句(从句谓语动词一般用过去时)5)It is/has been+一段时间+since从句(从句用一般过去时) It was/had been+一段时间+since从句(从句用一般过去完成时)【考纲要求】时态与语态一直是热点,也是广大考生复习备考的难点。
考纲要求考生应该具备较强的语言应用能力,能在具体语境中恰当、准确地使用某一特定时态;熟练掌握常见的8种时态,弄清16种时态,同时还要熟练运用特殊时态句式和用法以及不用被动式但表示被动的动词和短语。【教法指引】高考对时态的考查非常灵活且难度较大,不易把握。
大部分时态题答案的选择取决于题干语境;但也有部分时态试题较易把握,其用法相对固定,常见于特定句式结构中;还有部分常见时态用法特殊。综观近年来的高考单项填空题,动词成为考查的热点,在15个单项选择中,考查动词时态的题一般不少于2道,动词的时态常和语态、主谓一致结合在一起进行考查。
教师在指导学生复习备考、答题中,要遵循如下思路:① 这个动作可能发生在什么时间?题干句中可参照的时间信息有那些?② 这个动作处于什么时态,是进行中,还是已经结束(完成)?限制或修饰这个动作的状语信息有哪些?③ 这个动作与主语的关系,是主动还是被动?只要全面细致地考虑了这些问题的答案,试题的正确答案也就水落石出了。【知识网络】 动词时态与语态一、动词时态 (一)一般现在时 一般现在时常以动词原形表示,但当主语是第三人称单数时,应用动词的单数第三人称形式。
一般现在时主要有以下几种用法:1、一般现在时表示现在经常发生或习惯性的行为或状态,常与usually, always, every day, twice a week, seldom, sometimes等时间状语连用。 He always sleeps with the windows open.他总是开着窗子睡觉。
2、一般现在时表示主语的性格、特征、能力等。He works hard .他工作很努力3、一般现在时表示客观事实或普遍真理,也用在格言中。
The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。4、在时间、条件、比较等状语从句中表将来的动作 在由when, if, after, before, as, as soon as, the minute, the next time, in case, though, till, until, unless, so long as, where, whatever, whenever等引导的状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时,但应注意,主句的谓语动词必须用一般将来时。
The volleyball match will be put off if it rains. 如果下雨,排球赛将推迟5、表示安排或计划好的将来动作,通常限于表示"运动"的动词,如:go, come, leave, start等。The train starts at 10 o' clock in the morning.火车在上午10点发车(二)一般过去时 一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或状态,常和表示过去的时间连用,yesterday, last night, in 1990, two days ago等。
也表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, always等表示频度的时间状语连用1、表示过去某个特定时间发生的动作或状态,常有明确的时间状语,如yesterday,last night, some years ago,in1890等,以及由when等引导的时间状语从句。2、表示过去某一段时间内经常或反复发生的动作常与often,usually,seldom等表示频度的副词连用。
When I was in the countryside, I often called on my old friends there.我在乡村里,经常去拜访那里的朋友。3、在条件、时间状语从句中,常用一般过去时代替过去将来时。
They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him.他们说如果听到什么关于他的消息,就通知我们。4、表示虚拟语气这一用法只适用于某些特定的句型,表示现在或将来的非真实、主观意图或愿望。
If only I had a better memory.要是我的记忆力好一点就好了。If it rained tomorrow, the match would be put off.要是明天下雨,比赛就会延期举行。
(三)一般将来时1、一般将来时表示将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示将来的时间状语连用,如tomorrow, in the future, next year等。一般将来时由"助动词will/shall+动词原形"构成。
2、一般将来时的其他表达法(1)"be going to+动词原形"表将来①这种结构表示打算、计划、决定要做的事或肯定要发生的事。They are going to meet outside the school gate。
3.英语中常见的几种时态
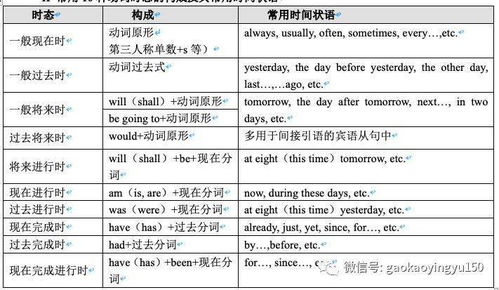
英语时态分为16种:一般现在、一般过去、一般将来、过去将来时,以及这四者的进行时、完成时和完成进行时 下面就英语中常见的八种基本时态进行阐述,其它的时态都是在这八种时态的基础上结合而成的。
一、一般现在时: 1。概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
2。时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, 3。
基本结构:动词 原形 (如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式) 4。 否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
5。一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
6。例句:。
It seldom snows here。 He is always ready to help others。
Action speaks louder than words。 二、一般过去时: 1。
概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 2。
时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week,last(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc。 3。
基本结构:be动词;行为动词 的过去式 4。否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
5。一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
6。例句:She often came to help us in those days。
I didn't know you were so busy。 三、现在进行时: 1。
概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 2。
时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc。 3。
基本结构:am/is/are+doing 4。否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing。
5。一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6。例句: How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons。
四、过去进行时: 1。概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2。时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3。基本结构:was/were+doing 4。
否定形式:was/were + not + doing。 5。
一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。 6。
例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit。 When he came in, I was reading a newspaper。
五、现在完成时: 1。概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2。时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years, etc。
3。基本结构:have/has + done 4。
否定形式:have/has + not +done。 5。
一般疑问句:have或has。 6。
例句:I've written an article。 The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years。
六、过去完成时: 1。概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2。时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc。
3。基本结构:had + done。
4。否定形式:had + not + done。
5。一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6。例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left。
By the end of last month。 We had reviewed four books 七、一般将来时: 1。
概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。 2。
时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc。 3。
基本结构:am/is/are/going to + do;will/shall + do。 4。
否定形式:was/were + not; 在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 5。
一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。 6。
例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies。 It is going to rain。
八、过去将来时: 1。概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2。时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc。
3。基本结构:was/were/going to + do;would/should + do。
4。否定形式:was/were/not + going to + do;would/should + not + do。
5。一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6。例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day。
I asked who was going there 。 九。
将来完成时: 1。概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态 2。
时间状语:by the time of;by the end of+时间短语(将来);by the time+从句(将来) 3。 基本结构:be going to/will/shall + have done 十。
现在完成进行时: 1。概念:在过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直持续到说话为止 2。
基本结构:have/has +been+doing 几种常见时态的相互转换 英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式: 十一、一般。
4.英语时态的入门书(基础)
英语时态的入门书(基础):推荐张满胜的驾驭语法系列,它总共有三部,走进语法、通悟语法、驾驭语法。很薄,但绝对是经典。张满胜也是语法教师中的翘楚。
初级是《走进语法》,内容如下:
第一章 英文基本句型
1.英文句子构成:主语部分+谓语部分
2.语+系动词+主语补足语(或者称作表语)
3.主语+谓语(+状语)
4.主语+谓语+宾语
5.主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语
6.主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语
第二章 动词分类
7.(情态)助动词和实义动词
第三章 句子的变化
8.陈述句的否定
9.一般疑问句
10.特殊疑问句
第四章 英文时态
(一):一般动作
11.一般现在时态的两种基本用法
12.一般现在时的其他用法
13.一般过去时基本用法
14.一般将来时态的三种用法
第五章 英文时态
(二):进行动作
15.进行时态的构成与意义
16.现在进行时基本用法
17.过去进行时基本用法
18.将来进行时基本用法
第六章 句词
19.名词短语
20.名词的定义及分类
21.可数名词与不可数名词
22.可数名词复数变化规则
23.不可数名词
24.不可数名词的度量
25.名词所有格的构成
相关推荐
声明:本网站尊重并保护知识产权,根据《信息网络传播权保护条例》,如果我们转载的作品侵犯了您的权利,请在一个月内通知我们,我们会及时删除。
蜀ICP备2020033479号-4 Copyright © 2016 学习鸟. 页面生成时间:3.485秒









